

Talking about sexual health can feel overwhelming, but being informed is the first step to taking charge of your well-being. An open and honest discussion about Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) is crucial for your health and your partners’.
In Singapore, understanding the symptoms, testing options, and available treatments empowers you to make responsible decisions.
This information will guide you through the essentials of STD symptoms, testing procedures, and effective treatments, giving you the confidence to manage your sexual health.
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs), often called STDs, are infections spread from one person to another through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex.
These infections come in various types, caused by different bacteria, viruses, or parasites. In Singapore, some of the most common ones we encounter are:
This is a bacterial infection that can often be quite sneaky, as it might not show any symptoms at all! It can affect both men and women, potentially leading to serious health issues like infertility if left untreated.
Another very common bacterial infection, similar to Chlamydia in that it can also be asymptomatic in many cases. It can affect the genitals, rectum, and throat.

This bacterial infection is a bit different because it progresses in distinct stages if it’s not treated. Early detection and treatment are crucial to prevent more severe health complications down the line.
Caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV), this viral infection is known for causing sores or blisters around the genitals or mouth. Genital herpes is important to remember that while symptoms can be managed, the virus stays in the body.
A very widespread virus, HPV can cause conditions like genital warts. More significantly, certain types of HPV are also linked to various cancers, including cervical cancer, which makes vaccination and regular screening vital.
This serious virus gradually attacks the body’s immune system, making it harder to fight off infections. Early diagnosis and consistent treatment can help individuals with HIV live long, healthy lives.
These are viral infections that specifically target the liver. While Hepatitis A is often spread through contaminated food or water, Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C can be transmitted sexually, among other ways.

This is a common and treatable infection caused by a tiny parasite. Like many STIs, it can often go unnoticed, as many people don’t experience any symptoms.
STDs are a significant public health concern. Understanding how they spread, their symptoms, and treatments is essential for raising awareness, preventing new cases, and ensuring timely care.
Crabs, or pubic lice, are tiny insects that infest pubic hair and sometimes other coarse body hair. They spread through close physical or sexual contact. Symptoms include intense itching and visible lice or eggs. Crabs can be treated with over-the-counter or prescription creams, lotions, or shampoos.
Mgen is a bacterial STI that often shows no symptoms, though some may experience painful urination or discharge. If untreated, it can lead to complications like pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) in women. Diagnosis requires specific tests, and it is treated with antibiotics.
Molluscum contagiosum is a viral skin infection causing small, firm bumps with a central dimple. It spreads through skin contact or contaminated items. While it usually clears on its own, topical treatments or minor procedures can speed up recovery.
NGU is urethral inflammation not caused by gonorrhea, often due to bacteria like chlamydia or Mgen. Symptoms include painful urination, discharge, or itching. It is treated with antibiotics after identifying the cause through tests.

Scabies is a highly contagious skin condition caused by mites burrowing into the skin. Symptoms include severe itching, especially at night, and a pimple-like rash. It spreads through close contact and is treated with prescription creams or lotions.
Jock itch, or tinea cruris, is a fungal infection in the groin area causing a red, itchy, ring-shaped rash. It thrives in warm, moist environments and can spread through contact or shared clothing. Over-the-counter antifungal treatments and keeping the area clean and dry are effective remedies.
Vulva or vaginal itching can stem from infections like yeast or bacterial vaginosis, allergic reactions, or irritations. Diagnosis is key to identifying the cause, and treatments include antifungal or antibacterial medications, creams, or lifestyle adjustments.
STIs are a global and local health concern, with consistent yearly cases of infections like chlamydia and gonorrhea in Singapore. These figures highlight the importance of regular testing as a responsible step for anyone sexually active.
One of the trickiest things about STDs is that they don’t always show clear signs. In fact, many STDs can be completely asymptomatic, meaning you could have an infection without ever knowing it. This is why regular testing is so important.
However, when symptoms do appear, they might include:
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s crucial to see a doctor as soon as possible. But remember, the absence of symptoms doesn’t mean you are necessarily in the clear. The only way to know your status for certain is to get tested.

Taking charge of your sexual health is vital for your overall well-being. Getting an STD test in Singapore, even if it feels a little awkward, is a responsible and empowering step.
Regular testing effectively manages your sexual health. Early detection allows for prompt treatment, often curing STDs or managing viral ones.
And prevents serious long-term complications like infertility or certain cancers. Testing also protects your partners; knowing your status helps prevent infection spread, demonstrating respect and responsibility for yourself and those you care for.
Self-STD testing can be a reliable and convenient option, especially if you value privacy or have a busy schedule. These test kits are designed to be user-friendly and provide accurate results when you follow the instructions carefully.
While self-testing is an empowering first step, I always recommend consulting a doctor to confirm your results and discuss the next steps. It’s reassuring to know these accessible tools can make managing your sexual health less intimidating.
So, who should get tested? Anyone who is sexually active, particularly if you have new or multiple partners. If you’re in a long-term relationship, getting tested at the beginning can also provide valuable peace of mind.
I understand there can be a stigma around STD testing, but I encourage you to view it as a routine part of your healthcare—just like a dental check-up.
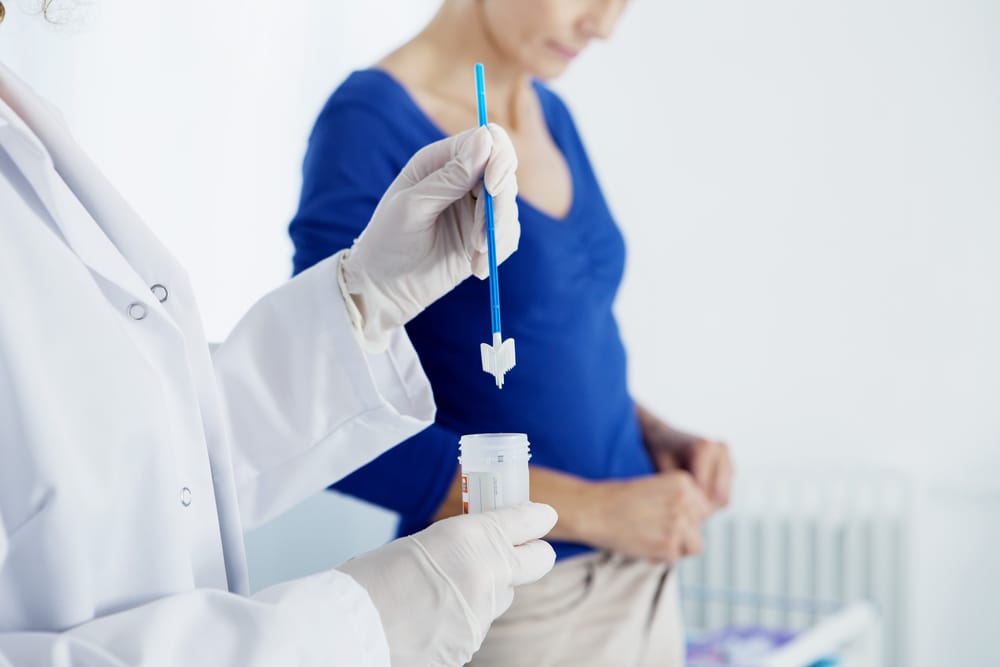
At Mediway Medical, we aim to make testing simple, discreet, and comfortable. Based on your sexual history and any symptoms, different tests may be recommended. Common methods include:
All testing is confidential and accurate. Our team is here to guide you and answer any questions throughout the process.
If you’ve received an STD diagnosis, please know that effective treatments are available, and catching it early is key for the best outcome.
While testing and treatment are vital, prevention is always the best approach. You can significantly reduce your risk of contracting an STD by practicing safe sex. This includes:
Education and awareness are key to empowering yourself and your community to make safer choices.
Emergency contraception (EC) offers a safe and effective way to prevent pregnancy after unprotected sex or contraceptive failure. In Singapore, emergency contraception pills, often called the “morning-after pill,” are readily available at most pharmacies and clinics without a prescription.
EC works by delaying ovulation or preventing fertilisation, and is most effective when taken as soon as possible, ideally within 72 hours of unprotected sex. Remember, EC is not intended for regular use and does not protect against sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
We encourage you to consult a healthcare professional for guidance and to discuss long-term contraceptive methods for lasting protection and peace of mind.
Taking charge of your sexual health is a vital act of self-care for your overall well-being and peace of mind. At Mediway Medical, we’re here to provide professional, compassionate support every step of the way, ensuring you feel comfortable and understood.
Our services are designed with your needs in mind, offering:
Don’t let fear or uncertainty about sexual health stop you from looking after yourself. Reaching out is a sign of strength, and we’re here to guide you with understanding and expertise.
Your well-being is a journey, and every step you take toward being informed and proactive matters. Remember that knowing your STD status is an act of care for yourself and your partners.
If you have any questions or are ready to get tested, please don’t hesitate to reach out to us at Mediway Medical. We’re here to help you navigate your health with confidence and support.
Some of the most common STDs include chlamydia, gonorrhea, HPV, herpes, and HIV. They are primarily transmitted through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex.
It is generally recommended that all sexually active individuals get tested at least once a year. You might consider more frequent testing if you have multiple partners, a new partner, or engage in higher-risk sexual behaviors.
Many STDs, especially those caused by bacteria like chlamydia and gonorrhea, can be cured with antibiotics. Viral STDs like herpes and HIV cannot be cured but can be effectively managed with antiviral medication.
An STD test typically involves providing a urine sample, a blood sample, or a swab from the affected area. The process is quick, and our staff at Mediway Medical ensure it is as comfortable and confidential as possible.
Yes, many STDs are asymptomatic, meaning they show no symptoms at all. This is why regular testing is essential for anyone who is sexually active, as it’s the only way to be certain of your status.
Bus No: NS1, NS2, 2, 2A, 12, 12E, 33, 51, 54, 61, 63, 80, 124, 145, 147, 166, 174, 174E, 190, 197, 851, 851E, 961, 961M
Bus No: NS1, NS2, 51, 61, 63, 63A, 80, 124, 145, 166, 174, 174E, 197, 851, 851E, 961, 961M
Mon-Fri Before 5/6pm: $2.00 for 1st hr, $1.00 for next subsequent 30min from 7am to 5pm
Mon-Fri after 5/6pm: $3.21/entry from 5pm to 7am the following day
Sat: $2.00 for 1st hr, $1.00 for next subsequent 30min from 7am to 5pm, $3.21/entry from 5pm to 7am the following day
Sun/PH: $3.21/entry from 7am to 7am the following day