Chlamydia
Chlamydia is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI) that often shows no symptoms. When symptoms do occur, women may experience abnormal vaginal discharge, painful urination, pain during intercourse, lower abdominal pain, and bleeding between periods. Men may notice discharge from the penis, painful urination, and pain or swelling in one or both testicles, though this is less common. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to get tested and seek treatment promptly.
Gonorrhoea
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) that can affect both men and women. Women may experience increased vaginal discharge, painful urination, vaginal bleeding between periods, painful intercourse, and abdominal or pelvic pain. Men may notice discharge from the penis (white, yellow, or green), painful urination, and, less commonly, pain or swelling in one testicle.
Both genders can develop rectal infections, which may cause discharge, anal itching, soreness, bleeding, or painful bowel movements. Throat infections due to gonorrhea may result in a sore throat, though they are often asymptomatic. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to get tested and seek treatment promptly.
Trichomoniasis (Trich)
Trichomoniasis, commonly known as trich, is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the parasite Trichomonas vaginalis. Symptoms can vary between men and women, and some individuals may not show any symptoms.
For women, symptoms may include unusual vaginal discharge (which may be clear, white, yellowish, or greenish), a foul-smelling vaginal odor, genital itching or irritation, painful urination, discomfort during intercourse, and vaginal redness or swelling.
For men, symptoms may include discharge from the penis, a burning sensation after urination or ejaculation, and irritation or itching inside the penis.
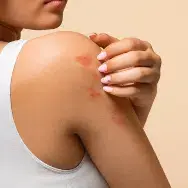
Syphilis
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) that progresses through several stages, each with distinct symptoms. In the primary stage, individuals typically develop a single sore (chancre) or multiple sores at the infection site, which are usually painless and firm, appearing within three weeks of exposure. During the secondary stage, symptoms can include skin rashes (often on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet), mucous membrane lesions, fever, swollen lymph nodes, sore throat, patchy hair loss, headaches, weight loss, muscle aches, and fatigue.
In the latent stage, no visible symptoms are present, and this stage can last for years. If left untreated, syphilis can progress to the tertiary stage, which may occur decades after the initial infection and can cause severe medical problems affecting the heart, brain, and other organs. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is crucial to get tested and seek treatment promptly.
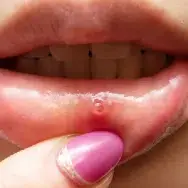
Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV)
Herpes is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV), which includes two types: HSV-1, typically causing oral herpes, and HSV-2, typically causing genital herpes. Symptoms can vary widely, and some individuals may not experience any symptoms.
Oral herpes (HSV-1) symptoms can include painful blisters or sores on the lips, mouth, or gums, an itching or burning sensation around the mouth, swollen lymph nodes, fever, sore throat, and headache.
Genital herpes (HSV-2) symptoms can involve painful blisters or sores on the genital or anal area, an itching or burning sensation in the genital area, painful urination, swollen lymph nodes in the groin, and flu-like symptoms such as fever and body aches.
For both types, symptoms may recur periodically, especially during times of stress or illness. Initial outbreaks are often more severe, with subsequent outbreaks being milder and shorter in duration. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to get tested and seek treatment promptly.
Hepatitis A / B / C
Hepatitis A, B, and C are viral infections affecting the liver, with similar symptoms but different modes of transmission.
Hepatitis A
- Transmission: Contaminated food or water, sexual contact with an infected person
- Symptoms: Fatigue, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain (upper right side), loss of appetite, low-grade fever, dark urine, joint pain, jaundice
Hepatitis B
- Transmission: Contact with infected body fluids (blood, vaginal secretions, semen)
- Symptoms: Abdominal pain, dark urine, fever, joint pain, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, weakness, fatigue, jaundice
Hepatitis C
- Transmission: Blood-to-blood contact (sharing needles, unsterilized medical equipment)
- Symptoms: Easy bleeding and bruising, fatigue, poor appetite, jaundice, dark urine, itchy skin, fluid buildup in the abdomen, leg swelling, weight loss, confusion, drowsiness, slurred speech, spider-like blood vessels on the skin
Non-Gonococcal Urethritis (NGU)
Non-Gonococcal Urethritis (NGU) is an inflammation of the urethra not caused by gonorrhea. It is typically caused by other infections, such as >Chlamydia trachomatis or >Mycoplasma genitalium.
For Men:
- Discharge from the penis, which may be clear or cloudy
- Burning sensation or pain during urination
- Itching or irritation at the opening of the penis
- Discomfort or pain in the lower abdomen
- Frequent or urgent need to urinate
For Women:
- Often asymptomatic
- Mild discomfort or burning during urination
- Unusual vaginal discharge