How is Herpes simplex virus (HSV) transmitted?
Herpes (HSV) is transmitted through direct contact with an infected person’s skin or mucous membranes. Key points of transmission include:
- Oral-oral contact: Kissing or sharing personal items like toothbrushes or eating utensils can spread HSV-1.
- Oral-genital contact: Oral sex can transmit HSV-1 to the genital area and HSV-2 to the mouth.
- Genital-genital contact: Sexual intercourse or genital contact can spread HSV-2.
- Mother-to-child transmission: A pregnant woman with an active HSV infection can pass the virus to her baby during childbirth, leading to neonatal herpes, which can be severe.
What are the symptoms of HSV infections?
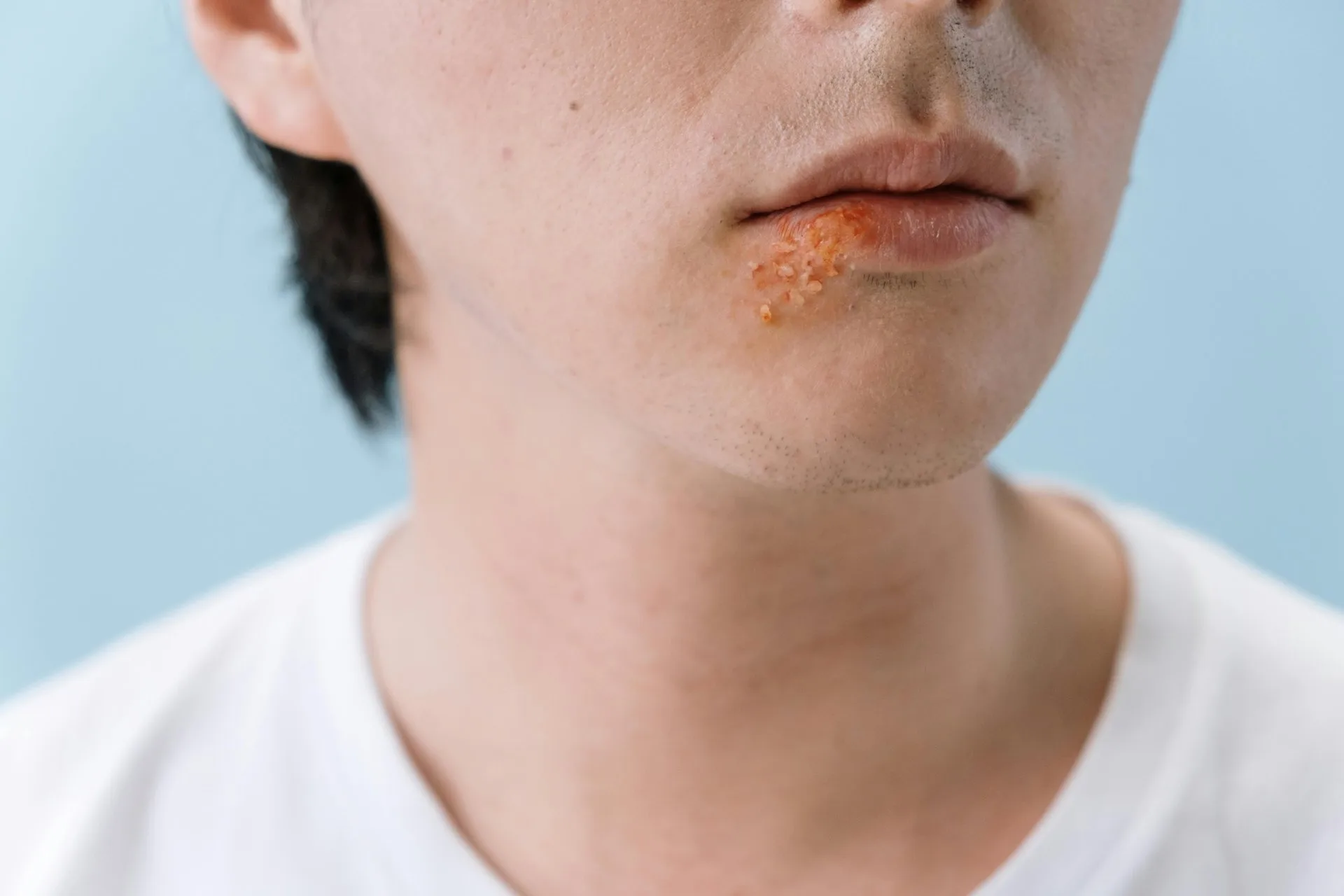
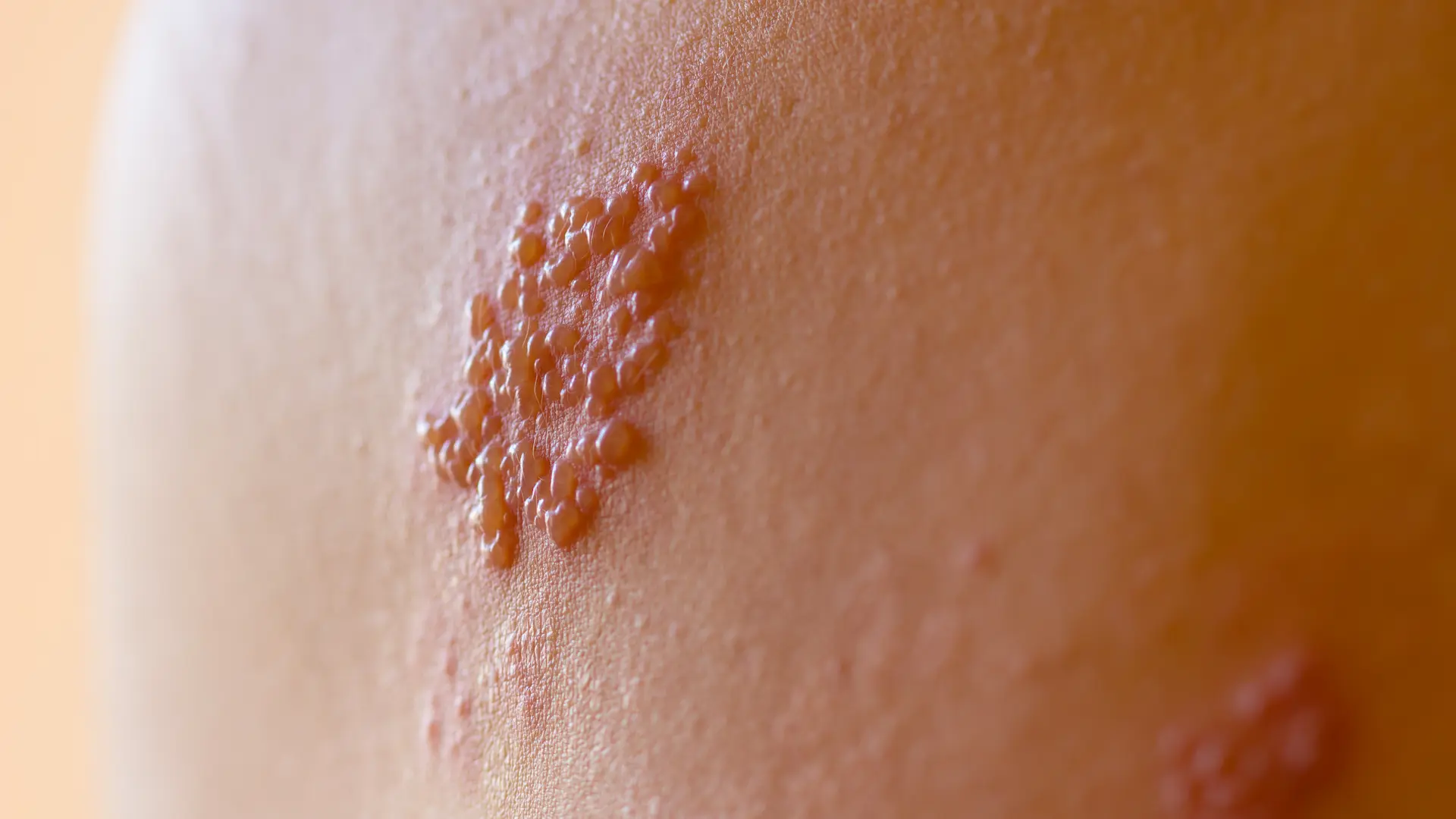
Symptoms of herpes simplex virus (HSV) can vary, and some people may not have any symptoms at all. When symptoms do occur, they typically appear within 2 to 12 days after exposure and may include:
- Painful blisters or sores on the lips, mouth, genitals, or anus
- Itching or burning sensation in the affected area
- Flu-like symptoms such as fever, body aches, and swollen lymph nodes
- Pain during urination if the sores are in the genital area
- Red, cracked, or swollen gums or sores inside the mouth (for oral herpes)
These symptoms can recur, with outbreaks triggered by factors such as stress, illness, or a weakened immune system.
What are the complications of untreated Genital Herpes?
If left untreated, genital herpes can lead to several complications, including:
- Recurrent Outbreaks: Frequent and painful recurrences of sores.
- Psychological Impact: Emotional distress, anxiety, and depression due to the stigma associated with the
infection. - Increased Risk of HIV: Genital herpes can increase the risk of contracting and transmitting HIV.
- Neonatal Herpes: Severe infection in newborns if the mother has an active infection during childbirth.
How is Herpes diagnosed?
HSV can be diagnosed through various methods, including:
- Physical Examination: A healthcare provider examines the sores and symptoms.
- Swab Test: A sample from a sore is tested in a laboratory to detect the virus.
- Blood Test: Blood tests can detect antibodies to HSV-1 and HSV-2, indicating a past or current infection.
How is Herpes (HSV) treated?
Herpes (HSV) is treated with antiviral medications. These medications help reduce the severity and frequency of symptoms but do not cure the infection. Common treatments include:
- Antiviral medications: Drugs like acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir can reduce the severity and
duration of symptoms. - Suppressive therapy: Daily antiviral medication can help prevent recurrent outbreaks and reduce the risk
of transmitting the virus to others. - Episodic treatment: Antiviral medication taken at the onset of symptoms can shorten the duration of an
outbreak.
Can Herpes (HSV) be prevented?
Yes, herpes simplex virus (HSV) can be prevented through a combination of safer sex practices and regular health monitoring:
- Use Condoms: Consistently using condoms during sexual activity can reduce the risk of transmission,
though it does not completely eliminate it. - Avoid Sexual Contact During Outbreaks: Refrain from sexual activity when symptoms or sores are present to
minimize the risk of spreading the virus. - Regular STI Screenings: Routine screenings can help detect infections early and prevent transmission to
partners. - Open Communication: Discuss HSV status and risks with sexual partners to make informed decisions about
precautions and treatment options. - Antiviral Medication: Taking antiviral medication as prescribed by a healthcare provider can reduce the
frequency of outbreaks and the risk of transmission.